Ovulation Induction
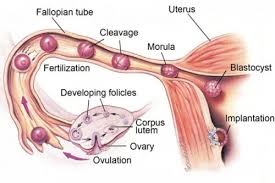
When an egg is released from one of the ovaries, this is known as ‘ovulation’. In women with regular menstrual cycles, this happens approximately once a month. In some women, the follicles that hold the eggs don’t mature regularly and so the woman ovulates irregularly, rarely or not at all.
Ovulation induction is a straightforward fertility treatment that involves taking oral or injectable medication to stimulate regular ovulation. The medication is usually taken at the beginning of the menstrual cycle and the body’s response is monitored through the cycle using ultrasound. The clinician can then see when you are due to ovulate and therefore the best time for intercourse or insemination.
Ovulation Induction medications include clomiphene citrate. This oral drug promotes the growth of the fluid-filled sacks (follicles) containing the eggs. If you do not ovulate, or you ovulate and do not become pregnant after clomiphene therapy, other medications known as gonadotropins may be prescribed, either alone or in combination. Gonadotropins are taken by injection under the skin. They replace natural follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), and if they are successful the ovaries produce multiple follicles and high-quality, mature eggs. Your hormone levels and follicular development are tracked throughout the stimulation cycle. If required, your medication protocol (the type and dose) may be altered for optimum results.
- Clomiphene Citrate (Clomid or Serophene) – Prescribed to women with infrequent periods and long ovulation cycles, it blocks the effects of estrogens and causes the body to produce more follicle-stimulating hormone.
- Human Menopausal Gonadotropin – Stimulating the development of multiple follicles and eggs during an ovulation cycle, hMG is derived from the urine of postmenopausal women.
- Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH) – Stimulating development of the fluid-filled sacks containing the eggs, this drug is available in a natural form, derived from the urine of postmenopausal women, or as a “recombinant or manufactured drug”.
- Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG) – Produced by the placenta during pregnancy and extracted from the urine of pregnant women, hCG triggers ovulation, releasing the eggs.
