Pelvic Masses
 The most common reason (outside of pregnancy) the uterus would become enlarged in a girl or young woman is due to accumulation of menstrual blood, also known as an outflow tract obstruction. Menstrual blood needs an exit from its origin in the endometrium (lining of the uterine cavity), through the cervix and out through the vagina. Any blockage along this pathway may result in an obstruction.
Birth defects involving the uterus, cervix, vagina or hymen may result in an obstruction. Uterine fibroids and adenomyosis are relatively common causes of uterine enlargement in adult women, but are infrequently seen in teens and younger adults.
The most common reason (outside of pregnancy) the uterus would become enlarged in a girl or young woman is due to accumulation of menstrual blood, also known as an outflow tract obstruction. Menstrual blood needs an exit from its origin in the endometrium (lining of the uterine cavity), through the cervix and out through the vagina. Any blockage along this pathway may result in an obstruction.
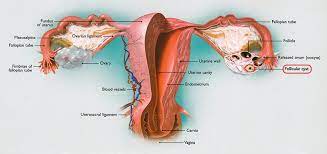
Birth defects involving the uterus, cervix, vagina or hymen may result in an obstruction. Uterine fibroids and adenomyosis are relatively common causes of uterine enlargement in adult women, but are infrequently seen in teens and younger adults. - Ovarian cysts – An ovarian cyst is a fluid-filled sac that develops on an ovary. They are painless, and patients do not experience symptoms.
- Ovarian cancer – Ovarian cancer occurs when abnormal cells in an ovary multiply, forming a tumor. The tumor can grow and spread to other body parts. Some of the symptoms of ovarian cancer include fatigue, heartburn, back pain, constipation, painful sexual intercourse, irregular periods, and indigestion.
- Benign ovarian tumor – Ovarian tumors are the abnormal growth of cell or lump. Unlike the cysts, they have fluid. If the cells in the ovarian tumor are not cancerous, the tumor is a benign tumor. That means the tumor will not spread to or invade surrounding tissues. Based on the tumor’s size, you may or not experience symptoms.
- Ectopic Pregnancy – This type of pregnancy occurs when fertilized eggs are implanted in the oviduct instead of the uterus. Normally, ectopic pregnancies do not grow to maturity. If the fertilized ovum continues growing in your fallopian tube, your tube will rupture and result in heavy bleeding. It can also lead to internal bleeding and severe and sudden pain. If left untreated, an ectopic pregnancy might be fatal.
- Pelvic inflammatory disease – It happens due to an infection. It is an inflammation of the upper genital tract that includes ovaries, uterus, and oviduct.
- Ovarian torsion – It is an emergency that involves a partial or complete rotation of tissues that support your ovary, which stops blood flow to the ovary.
- Tubo – ovarian abscess- It is an infectious mass that forms due to pelvic inflammatory ailment.
- Painful periods
- Abnormal bleeding from your uterus
- Abnormally heavy bleeding during periods
- Severe pelvic or abdominal pain which is on one side
- Urinary or incontinence frequency and urgency
- Loss of energy
- Weight loss
- Fever
- Fatigue
- Vaginal discharge
Treatment of a pelvic mass depends on the nature of the mass. While most ovarian cysts will resolve spontaneously, other causes will most likely require surgical intervention with focus on addressing the underlying abnormality and preserving/maximizing reproductive function and potential.
