Ovarian Cyst
 Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that grow inside or on top of one (or both) ovaries. A cyst is a general term used to describe a fluid-filled structure. Ovarian cysts are usually asymptomatic, but pain in the abdomen or pelvis is common.
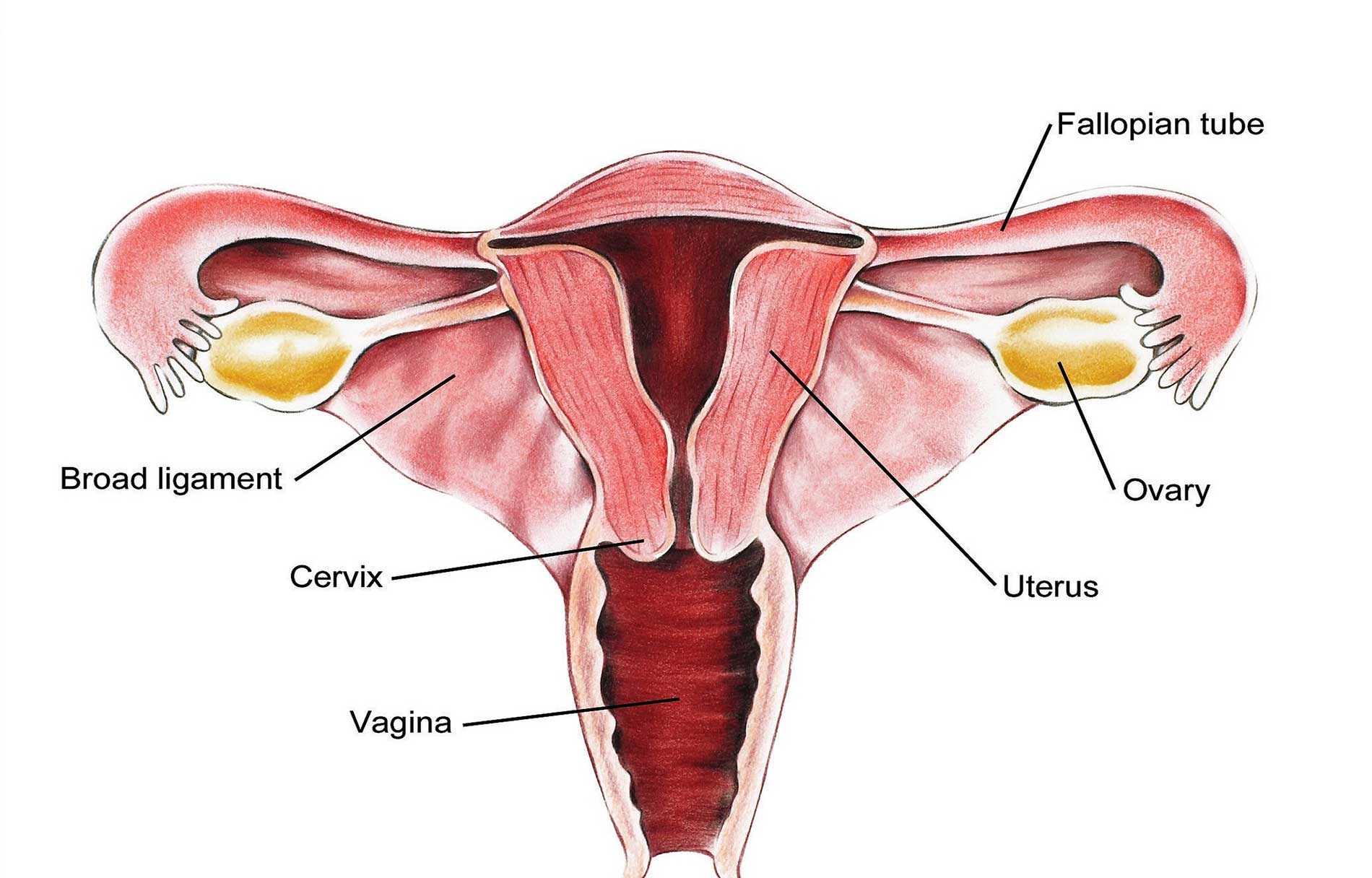
The ovaries are part of the female reproductive system. They’re located in the lower abdomen on both sides of the uterus. Women have two ovaries that produce eggs as well as the hormones estrogen and progesterone. Sometimes, a fluid-filled sac called a cyst will develop on one of the ovaries. Many women will develop at least one cyst during their lifetime. In most cases, cysts are painless and cause no symptoms.
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs that grow inside or on top of one (or both) ovaries. A cyst is a general term used to describe a fluid-filled structure. Ovarian cysts are usually asymptomatic, but pain in the abdomen or pelvis is common.
The ovaries are part of the female reproductive system. They’re located in the lower abdomen on both sides of the uterus. Women have two ovaries that produce eggs as well as the hormones estrogen and progesterone. Sometimes, a fluid-filled sac called a cyst will develop on one of the ovaries. Many women will develop at least one cyst during their lifetime. In most cases, cysts are painless and cause no symptoms. - Functional Cysts
- Benign Neoplastic Cysts
- Endometriotic Cysts
- Malignant Cysts
In the early stages of every menstrual cycle, your ovaries normally develop small cyst-like structures called follicles – when you ovulate, an egg is released from one of these follicles. If a normal follicle keeps on growing, it becomes a ‘functional cyst’. This type of cyst usually disappears within two or three cycles.
Factors that increase your risk of developing ovarian cysts include hormone changes (including fertility drugs), pregnancy, endometriosis and a severe pelvic infection that spreads to your ovaries.
- Abdominal bloating or swelling
- Painful bowel movements
- Pelvic pain before or during the menstrual cycle
- Painful intercourse
- Pain in the lower back or thighs
- Breast tenderness
- Severe or sharp pelvic pain
- Fever
- Faintness or dizziness
- Rapid breathing
- Nausea and vomiting
